Ventilation and Heating Systems
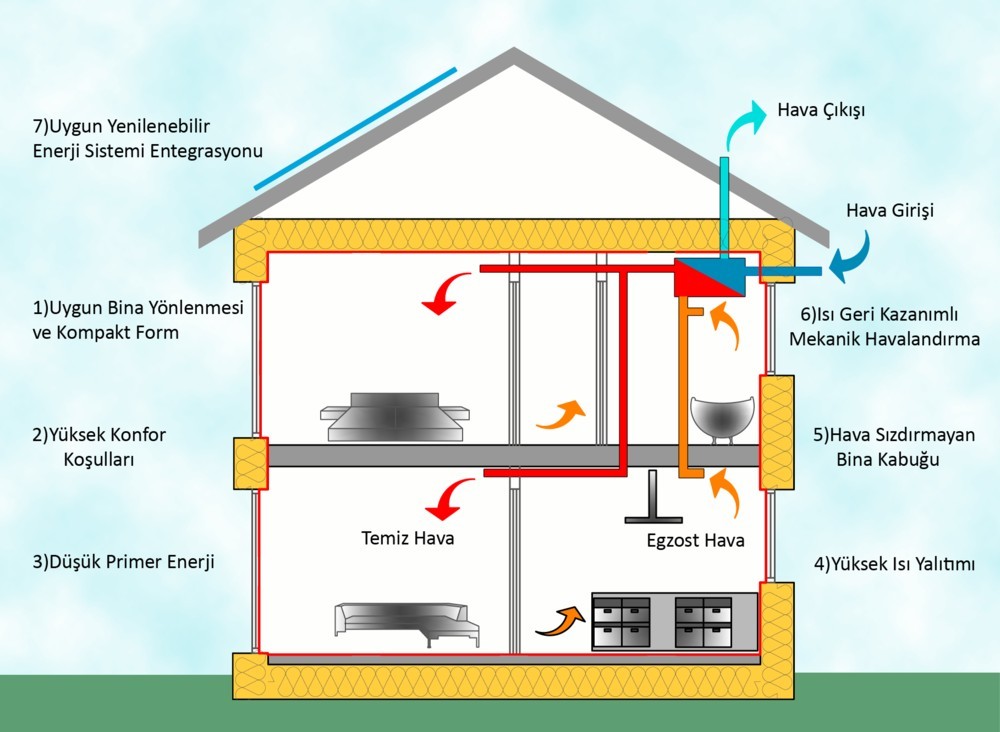
What are Ventilation Systems?
Ventilation systems are a set of technologies and solutions used to maintain the health and comfort of people living or working in enclosed spaces. These systems help improve indoor air quality, expel harmful substances and polluted air, and allow fresh air to enter the space. Ventilation is not only used in buildings, but also in factories, laboratories, hospitals, schools, and shopping centers, among other enclosed environments. The main purpose of ventilation systems is to clean the air in the spaces where people live or work, keeping it breathable and healthy.
Ventilation systems work by expelling polluted air and harmful gases while introducing fresh air, thus creating a safe and healthy air environment indoors. Typically, ventilation systems serve to remove dust, smoke, carbon dioxide, ammonia, and other hazardous gases. These systems also regulate humidity levels within the space, controlling high humidity that could cause discomfort or sweating. As a result, ventilation systems do not just provide clean air, but also form the foundation for a healthy living and working environment.
There are various ventilation systems for different uses. The most important factors when choosing a system include the size of the area, the activities taking place in the environment, and environmental conditions. For example, industrial facilities require stronger airflow, while mechanical ventilation systems may suffice for offices and homes.
What is Thermal Insulation?
Thermal insulation is an application used in buildings to enhance energy efficiency, provide comfort, and reduce energy costs. It works by preventing heat transfer between two environments with different temperatures, ensuring that the interior of a building stays at a stable temperature. In winter, it blocks the cold air, and in summer, it prevents the entry of hot air, reducing energy consumption and creating a more comfortable living environment.
Thermal insulation is applied to the exterior facades of buildings, attics, window glazing, and door systems to minimize heat loss. Heat loss in buildings, particularly through walls, is substantial. To reduce this loss, thermal insulation is essential. Additionally, effective insulation is not limited to protecting against cold weather; it also helps maintain a cool indoor environment in areas with hot climates, reducing energy consumption.
Insulation materials are selected based on their thickness, depending on the temperature conditions of the climate. In regions with significant heat loss during winter, thicker insulation materials are used, while thinner materials are preferred in hotter climates. This application reduces both heating costs in winter and cooling costs in summer.
It is important to remember that energy used for cooling in the summer can exceed the energy consumed for heating in the winter. Therefore, maintaining a cool indoor environment in summer is also an important function of thermal insulation.
The fundamental principle of thermal insulation is that heat always moves from a warmer environment to a cooler one. Controlling this movement is crucial to preventing energy loss. Insulating a building ensures energy efficiency by preventing the interior heat from escaping and keeping the outdoor hot air from entering.
For Turnkey Projects, Contact Us Today!
